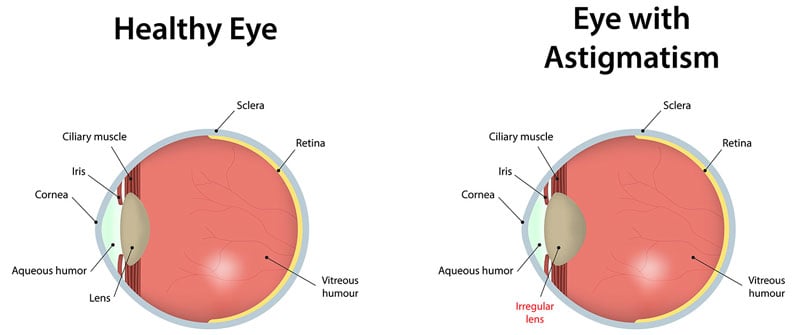
Astigmatism is a common vision condition that causes blurred vision. It occurs when the cornea (the clear front cover of the eye) is irregularly shaped or sometimes because of the curvature of the lens inside the eye.
An irregularly shaped cornea or lens prevents light from focusing properly on the retina, the light-sensitive surface at the back of the eye. As a result, vision becomes blurred at any distance. This can lead to eye discomfort and headaches.
Astigmatism frequently occurs with other vision conditions like myopia (nearsightedness) and hyperopia (farsightedness). Together these vision conditions are referred to as refractive errors because they affect how the eyes bend or “refract” light.
There are many causes to astigmatism. It can be hereditary and is usually present from birth. It can decrease or increase over time.
A comprehensive optometric examination will include testing for astigmatism. If necessary, your optometrist can provide eyeglasses or contact lenses that correct the astigmatism by altering the way light enters the eyes.
Another option for treating astigmatism is a corneal procedure called orthokeratology (ortho-k). In this painless, noninvasive procedure, the patient wears a series of specially designed rigid contact lenses to gradually reshape the curvature of the cornea.
Laser surgery can also treat some types of astigmatism. The laser changes the shape of the cornea by removing a small amount of eye tissue.
What causes astigmatism?
The curvature of the cornea and lens bends the light entering the eye in order to focus it precisely on the retina at the back of the eye. In astigmatism, the surface of the cornea or lens has a somewhat different curvature.
the surface of the cornea is shaped more like a football instead of round like a basketball, the eye is unable to focus light rays to a single point. Vision becomes out of focus at any distance.
In addition, the curvature of the lens inside the eye can change, resulting in an increase or decrease in astigmatism. This change frequently occurs in adulthood and can precede the development of naturally occurring cataracts.
Sometimes astigmatism may develop following an eye injury or eye surgery.
Astigmatism also occurs due to a relatively rare condition called keratoconus in which the cornea becomes progressively thinner and cone-shaped. This results in a large amount of astigmatism, which causes poor vision that cannot be clearly corrected with eyeglasses. People with keratoconus usually need contact lenses for clear vision and eventually may need a corneal transplant.
How is astigmatism diagnosed?
An optometrist can diagnose an astigmatism through a comprehensive eye examination. Testing for astigmatism measures how the eyes focus light and determines the power of any optical lenses needed to improve vision. This examination may include:
- Visual acuity-When you read letters on a distance chart, you are measuring your visual acuity. Visual acuity is given as a fraction (for example, 20/40). The top number is the standardized testing distance (20 feet) and the bottom number is the smallest letter size read. A person with 20/40 visual acuity would have to get within 20 feet to read a letter that should be seen clearly at 40 feet. Normal distance visual acuity is 20/20.
- Keratometry/Topography-A keratometer is the primary instrument used to measure the curvature of the cornea. By focusing a circle of light on the cornea and measuring its reflection, it is possible to determine the exact curvature of that area of the cornea’s surface. This measurement is particularly critical in determining the proper fit for contact lenses. A corneal topographer, which is gaining use, generates a contour map of the cornea and provides even more detail of the cornea’s shape.
- Refraction-Using an instrument called a phoropter, your optometrist places a series of lenses in front of your eyes and measures how they focus light. This is performed using a handheld lighted instrument called a retinoscope or an automated instrument that evaluates the approximate focusing power of the eye. Based on your responses, the power is then refined to determine the lenses that allow the clearest vision. Despite improved technology, patient input remains integral in determining vision needs.
With the information from these tests, your optometrist can determine if you have astigmatism. Your optometrist will use these findings, combined with those of other tests performed, to determine the power of any lens correction you need to provide clear, comfortable vision. Once testing is complete, your optometrist can discuss treatment options.
How is astigmatism treated?
People with astigmatism have several options to regain clear vision. They include:
- Eyeglasses. People with astigmatism primarily choose eyeglasses to improve their vision. The eyeglasses contain a special cylindrical lens prescription that compensates for the astigmatism. This provides additional power in specific parts of the lens.Generally, a single-vision lens is prescribed to provide clear vision at all distances. However, patients over age 40 who have presbyopia may need a bifocal or progressive addition lens.
- Contact lenses. Some people will have better vision with contact lenses rather than eyeglasses. Contact lenses may provide clearer vision and a wider field of view. However, since contact lenses are worn directly on the eyes, they require regular cleaning and care to safeguard eye health.Standard soft lenses may not be effective in correcting astigmatism. However, special toric soft contact lenses can correct for many types of astigmatism. Because rigid gas-permeable contact lenses maintain their regular shape while on the cornea, they can compensate for the cornea’s irregular shape and improve vision for people with astigmatism.
- Orthokeratology. Orthokeratology (ortho-k) involves the fitting of a series of rigid contact lenses to reshape the cornea. The patient wears contact lenses for limited periods, such as overnight, and then removes them. People with moderate astigmatism may be able to temporarily obtain clear vision without lenses for most of their daily activities. Orthokeratology does not permanently improve vision. If patients stop wearing the retainer lenses, their vision may return to its original condition.
- Laser and other refractive surgery procedures. Astigmatism can also be corrected by reshaping the cornea through LASIK (laser in situ keratomileusis) or PRK (photorefractive keratectomy). PRK removes tissue from the superficial and inner layers of the cornea. LASIK removes tissue only from the inner layer of the cornea.
If you have an astigmatism, you have a wide range of options to correct your vision problem. In consultation with your optometrist, you can select the treatment that best meets your visual and lifestyle needs.


